Growing and LeBlanc (2013) described the practice recommendation to make conditional discrimination training with autistic children.
One of the recommendations involved using datasheet specifically designed to provide a target stimulus that has been set for each experiment along with balancing the stimulus location if the three-item array of stimuli comparison.
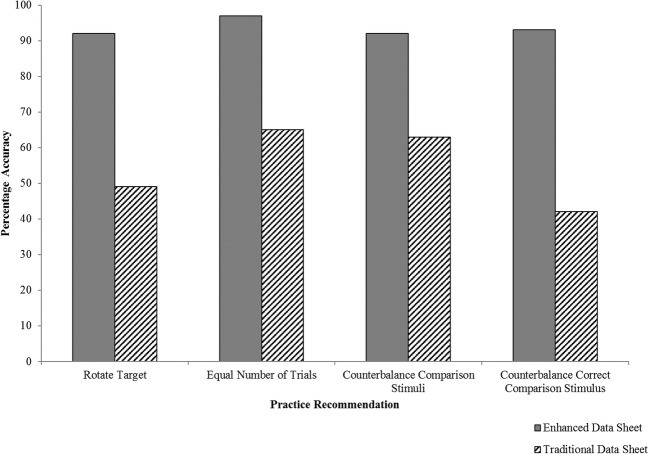
This study evaluates whether the recommended data sheet will cause a higher procedural integrity of trial balance sheet compared with standard data (ie, the target and the array is not pre-set). behavioral therapists forty-two institutions participating provider.
Participants were randomly assigned to either a standard data sheet conditions or conditions improved data sheet. Participants watch a short video about this growing and LeBlanc practice recommendations for task matching and orientation to the datasheet for the conditions laid down, and then implemented tasks in accordance with the confederation portion in the role of a child with autism.
enhanced data sheet resulting in a higher accuracy of implementation on the balance of standard data sheets, with the biggest difference to the rotation of the target stimulus in the trial and to balance the placement of the correct comparison stimulus in the array.
Catalog of NIMS creep data sheets.
Background NIMS Creep Data Sheet Project, together with the preliminary studies and facilities, material selection, and testing methods, are summarized. The results of the project are described, focusing on the long-term creep strength steel and austenitic ferritic heat resistant.
In some cases, the slope of the curve of stress versus time-to-rupture in the long run is different from that in the short term in a real way depending on the type of material. Heat-to-heat variation in creep strength is recognized for ferritic and austenitic steels, even when the chemical composition of the steel examined within the range of specifications.
The reason for the variation of the heat-to-heat differences in the chemical composition, the number of minor elements, and the grain size, among others. Their inherent creep strength is found in the very long term for ferritic heat resistant steel.
Small number of solute elements affect the inherent creep strength, independently of strengthening precipitates or dislocation structure. Point changes were observed in the tertiary creep stage for low alloy steels and for austenitic stainless steels when rainfall occurs during crawling. A region-splitting analysis method is proposed to evaluate the long-term creep strength of high-chromium ferritic steels.
This method is used to review the allowable stress of high chromium ferritic steels in Japan. A metallographic atlas, diagram of time-temperature-precipitation, and the fracture-mode map proposed for ferritic and austenitic steels on the basis of creep-rupture specimen.
